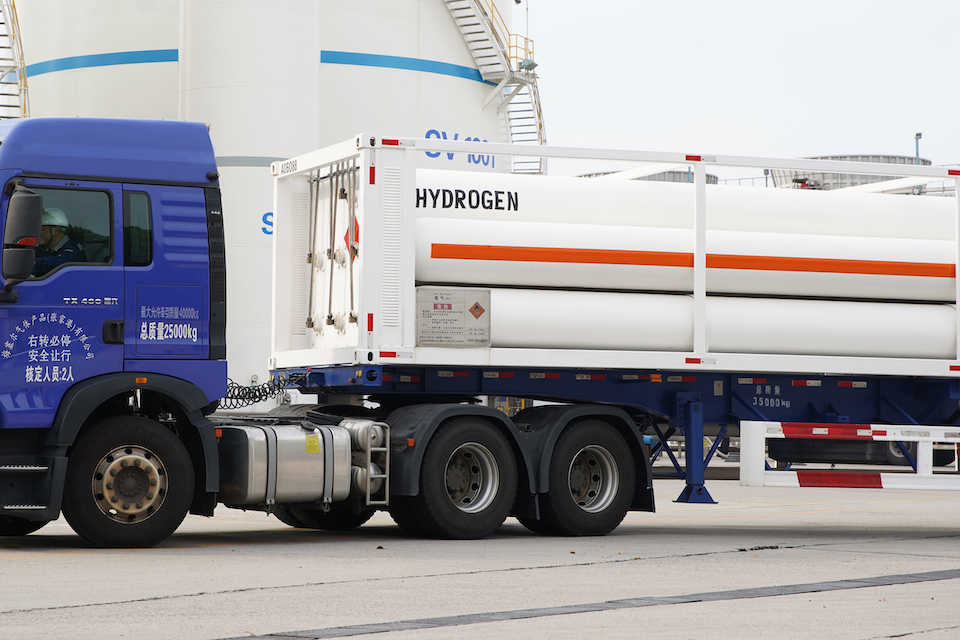
Hydrogen is the lightest element and most abundant chemical substance in the universe, playing a key role in the global transit toward cleaner energy systems. In China, Messer operates a network of hydrogen production facilities across strategic regions, ensuring a stable and reliable supply ranging from industrial-grade to high-purity hydrogen. Our comprehensive delivery solutions, including cylinders, tube trailers, and on-site generators, are tailored to meet evolving demands of industrial customers. Messer has extensive experience delivering high-purity hydrogen solutions for established industrial applications, and our team is also excited to be working at the forefront of new applications that will help hydrogen become a central pillar of a more sustainable economy. In traditional manufacturing fields such as metal heat treatment and float glass production, hydrogen is valued for its exceptional reducing property and high purity. It has long been used in processes including steel annealing, metal reduction, and glass melting. By effectively preventing oxidation, hydrogen enhances surface quality, particularly in the treatment of high-alloy steels, aluminum, and other advanced materials. Hydrogen plays an increasing role in high-tech industries such as electronics and aerospace. In processes like wafer annealing, epitaxial growth, and PERC solar cell passivation, hydrogen helps maintain ultra-clean environments. In OLED displays and the production of automotive-grade glass panels, hydrogen is used for surface cleaning and oxidation control, contributing to higher product yields and improved optical performance.
Supply Modes
Products Safety

Safety is a core value and embedded in everything we do at Messer. We are committed to the safe use of our products and set working standards that protect the safety and health of our customers, our people, and our communities.
What Are Safety Hazards Associated When Working with Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the lightest of all elements. When released as a gas, it quickly rises to the highest point in any enclosed space. Hydrogen presents some risk of asphyxiation. The gas itself isn’t toxic, but if too much of it builds up in an enclosed space, it displaces the oxygen, making the air unsafe. At high concentrations, hydrogen may also increase the risk of combustion or explosion. To ensure a safe operating environment, any facility using hydrogen should always be equipped with proper ventilation and atmospheric monitoring to ensure a safe operating environment.
Hydrogen is highly flammable and can be ignited with very little energy. When its concentration in air reaches 4%, it may cause combustion or even explosion. Hydrogen burns very quickly and almost invisibly. So, the best way to avoid a hydrogen fire is to eliminate all possible sources of ignition such as electrical sparks, electrostatic discharge, open flames, or high-temperature surfaces and to stop the source of hydrogen if a fire does occur.
You May Also Be Interested in